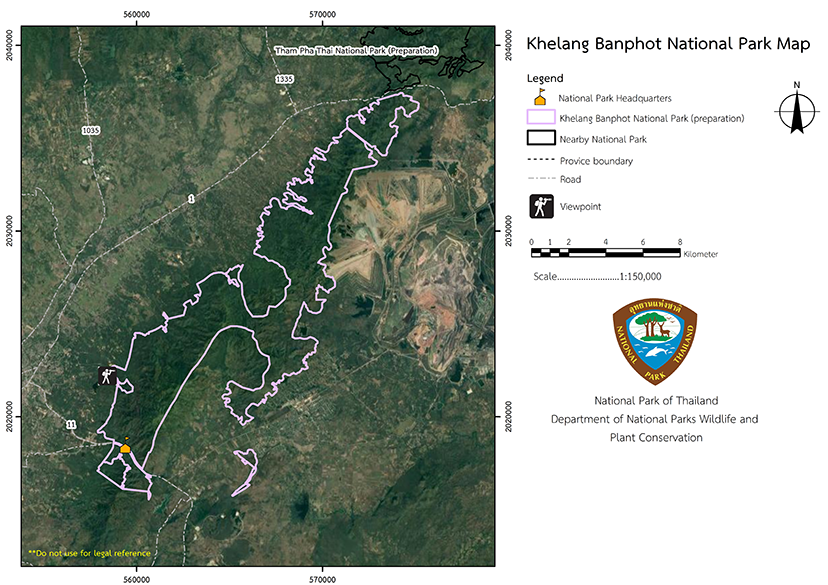
Khelang Banphot National Park (under gazetting)
Contact Location : Phrabat Arboretum, Moo 4, Phrabat Sub-district, Mueang District, Lampang Province
Telephone Number : (+66) 9 5451 7597
Email : salawinnp@hotmail.co.th
Facebook : Khelang Banphot National Park
Information
A survey was undertaken to help establish Khelang Banphot National Park which covers 3 National Reserved Forests;
1.) Mae Yang Mae Ang National Reserved Forest, located in the Mueang District, Lampang Province which has an area of approximately 34,626 rai or 21.64 square kilometers.
2.) Mae Chang National Reserved Forest, located in Mueang District, Lampang Province, which has an area of approximately 2,828 rai or 1.77 square kilometers.
3.) Mae Mo National Reserved Forest, located in Mae Mo District, Lampang Province, an area of approximately 12,311 rai or 9.28 square kilometers.
4.) Forested area in Phra Bat and Phichai Sub-district, Mueang District, Lampang Province, with an area of 624.14 rai or 1.00 square kilometers.
- The total area of approximately 50,390 rai or 80.62 square kilometers.
- The area encompasses a total of 7 Sub-districts, which are
1. Phra Bat Sub-district, Mueang District, Lampang Province
2. Phichai Sub-district, Mueang District, Lampang Province
3. Sadet Sub-district, Mueang District, Lampang Province
4. Mae Mo Sub-district, Mae Mo District, Lampang Province
5. Ban Khong Sub-district Mae Mo District, Lampang Province
6. Mae Tha Sub-district, Mae Tha District, Lampang Province
7. Huai Sua Sub-district, Mae Tha District, Lampang Province
Background
-
Note : After paying the entrance fee to the National Park, please carry the receipt for inspection.
50390 rai (80.6 square kilometers)
|
|
|
|
-
Welfare shop : -
Mobile phone signal:
National Park Headquarters area : AIS, TRUE
|
|
The mountainous region runs on a north-south axis and is comprised of a complex mountain landscape, with small and large mountains interspersed throughout. Elevations are between 400 -- 900 meters above sea level, with the highest summit known as Doi Farang (and previously Doi Ngam), which is 904 meters above sea level.
|
|
The months with the highest and lowest monthly mean temperatures in Khelang Banphot National Park were April and January, with 37.8 and 14.4 degrees Celsius, respectively. It rains for on average 111 days year, with July having the most rainfallwith 17 days. The averageannual rainfall total is 1,060 millimeters, with September the wettest month with 213.3 millimeters.
|
|
|
|
Forest Resources - The area is primarily covered by deciduous dipterocarp forest alternates with mixed deciduous forest and pine forests, sporadic pine forests on the mountain summit, which is 700 meters above sea level. As the area is mountainous there is abundant wildlife in the dense forests. The forest is fertile, provides habitat for small wild animals, and serves as a haven for them. According to a survey conducted the forest contains the following animals: 1) Ten species of mammals are found in this group including Leopard (Prionailurus bengalensis), Common Palm Civet (Priondpm erdocppr), Kloss's Mole (Euroscaptor klossi), Burmese Hare (Lepus peguensis), Wild Boar (Sus scrofa), Callosciurus caniceps , Chipmunk (Tupaia glis), Mongoose (Herpestes javanicus), and Bamboo Rat (Cannomus bedius). 2) Birds are common in the park, with 11 species in 9 families. They include Red Junglefowl (Gallus gullus), Red-Whiskered Bulbul (Pycmonotus jocosus), White-Rumped Shama (Copsychus malabaricus) Common Iora (Aegithina tiphia), Scarlet-Backed Flower Pecker (Dicaeum cruentatum), Greater Racket-Tailed Drongo (Dicrurus paradiseus), Lesser Racket-Tailed Drongo (Dicrurus remifer), Black Drongo (Dicrurus macrocercus), White-Faced Jay (Garrulus glandarius), Chinese Pond Heron (Ardeola bacchus), and Common Myna (Acridotheres tristis). 3) Amphibian wildlife includes 6 species in 4 families such as the Asiatic Burrowing Frog (Kaloula pulchra), Frog (Rana pilcata), Green Frog (Occidozyga lima), toads, Elongated Tortoise (Indotestudo clongata), and turtles. 4) Reptile wildlife includes 4 species in 3 families such as the Butterfiy lizards, lizards, Eastern Bent-Toed Gecko (Cyrtodactylus spp.), and Waterfall Dwelling Snake (Elaphe taeniura). 5) Four types of fish were found including the Dwarf Snakehead, Mastacembelus armatus , Dwarf Snakehead, Eel Garden, and Minnow. 6) Thirteen species ofinsects were found in the National Park area including Cheirotonus parryi, Violin Beetle (Mormolyce), Common Bluebottle butterfly (Graphium sarpedon), Green Drgontail butterfly (Lamproptera meges), Common Birdwing butterfly (Troides helena), and the Common Rose butterfly (Pachliopta aristolochiae). |
How to get there by car :
From Lampang town, take Highway No. 11 to Mae Tha District for about 8 kilometers, where visitors will see the sign for Phra Bat Arboretum. Turn left at the Arboretum sign and after 500 meters you will reach Khelang Banphot National Park Headquarters.
-